Understanding Identity Controls in the Cloud
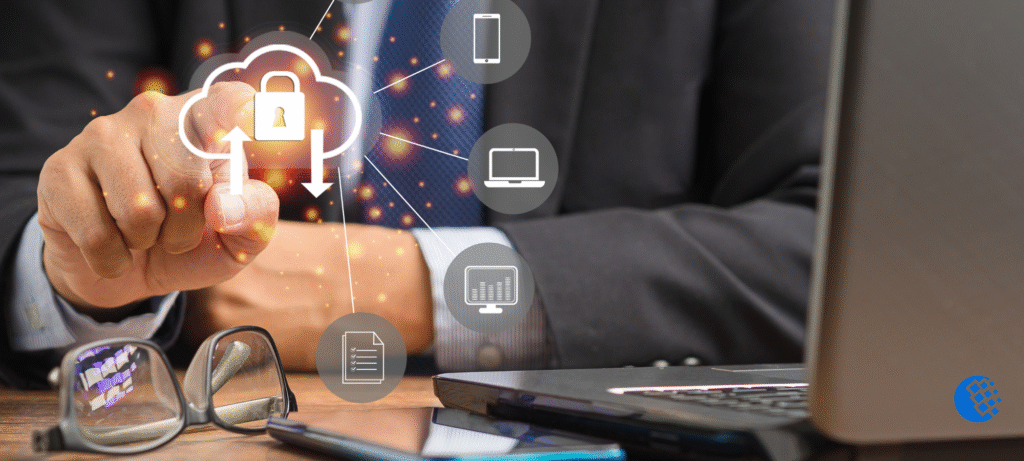
Identity controls are the tools and policies that manage who can access cloud resources. These controls help ensure only authorized people can use sensitive data and applications. As organizations shift more data and services to the cloud, strong identity controls are more important than ever to prevent unauthorized access, data leaks, and cyberattacks. Weak identity management can lead to costly data breaches, regulatory fines, and loss of customer trust. By focusing on identity controls, businesses can set a strong foundation for their overall cloud security strategy.
Start with Strong Authentication Methods
The first step to improving identity controls is to use strong authentication methods. Require multi-factor authentication (MFA) for all users, especially those with administrative access. MFA requires users to prove their identity in multiple ways, making it significantly harder for attackers to gain unauthorised access. For more information on cloud security, refer to these cloud security best practices for preventing ransomware attacks. When setting up authentication, select options that strike a balance between security and user experience. Passwords should be long, complex, and changed regularly. Consider using passphrases, which are easier to remember but difficult for attackers to guess. Biometric authentication, such as fingerprint or facial recognition, can also provide an additional layer of security. By strengthening how users prove their identity, you reduce the risk of stolen or guessed credentials leading to unauthorized access.
Set Up Role-Based Access Control (RBAC)
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) refers to granting users access based on their job roles. This limits who can view or change certain data. Assign permissions carefully so that each user has only the necessary access to perform their job. Regularly review and update these roles as people change positions or leave the company. For more guidance, the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) provides detailed advice on access controls:. RBAC also makes it easier to manage permissions at scale, especially in large organizations with many users and cloud services. By grouping users into roles and assigning permissions to those roles, you reduce the risk of granting excessive access to any one person. This approach also simplifies audits and compliance checks, as it allows you to easily identify who has access to what.
Monitor and Audit User Activities
Continuous monitoring helps you identify unusual activity that may signal a security issue. Set up logging to track who accesses what resources and when. Regularly review these logs for signs of unauthorized access or risky behavior. Automated tools can help quickly flag suspicious activities. In addition to real-time monitoring, set up alerts for activities such as failed login attempts, changes to permissions, or access from unfamiliar locations. These alerts can help you respond quickly to potential threats. Keeping detailed audit trails is also crucial for compliance and for investigating incidents that may occur.
Manage User Lifecycles Carefully
User accounts should be created, updated, and removed according to an individual’s employment status. Make sure accounts are disabled or deleted promptly when employees leave or change roles. This reduces the risk of old accounts being used by attackers. Having a clear process for onboarding and offboarding users is crucial to maintaining a secure cloud environment. Automated workflows can help ensure that account changes happen quickly and accurately, reducing the chance of forgotten or orphaned accounts. It’s also important to review service accounts and other non-human identities, as these are often overlooked and can become targets for attackers if not managed properly.
Use Least Privilege Principles
The principle of least privilege means granting users the minimum access necessary to perform their work. Avoid granting broad or unnecessary permissions. Review all user permissions regularly and remove any that are no longer needed. This practice helps limit the damage if an account is compromised. For more information on least privilege and cloud security, refer to the Centre for Internet Security’s recommendations. Implementing the principle of least privilege can be challenging, especially in rapidly changing environments, but it is one of the most effective ways to mitigate risk. Use tools that help you visualize and manage permissions, and schedule regular access reviews to keep your environment secure.
Educate Employees About Identity Security
Employees play a crucial role in maintaining the security of cloud systems. Provide regular training on how to recognize phishing, use strong passwords, and report suspicious activity. Ensure that everyone understands the importance of identity controls and how to adhere to your security policies. Training should be ongoing and updated to reflect new threats and best practices. Encourage a culture where employees feel comfortable reporting security concerns or mistakes. Phishing remains a top method for attackers to steal credentials, so regular simulations can help employees spot and avoid these attacks. The Federal Trade Commission (FTC) provides valuable resources for teaching employees about cybersecurity.
Automate Where Possible
Automation can help reduce human error and make identity management more efficient. Use automated tools to enforce policies, manage permissions, and respond to security incidents. Automated alerts can notify you quickly if there is an unusual login attempt or policy violation. Automation can also help with tasks like password resets, access reviews, and deprovisioning accounts, freeing up IT staff for more complex work. These tasks are often handled as part of ongoing IT operations by providers such as outsourceIT, which supports continuous monitoring, access management, and cloud infrastructure oversight for business environments. By automating routine identity management tasks, you improve consistency and reduce the chance of mistakes that could lead to security gaps.
Regularly Assess and Test Your Controls
Identity controls should be tested often to make sure they are working as intended. Conduct regular audits and use simulated attacks to find weaknesses. Update your policies and tools as threats evolve and your organization grows. Penetration testing and red team exercises can help you see how well your controls stand up to real-world attacks. Involve both internal and external experts to get a complete picture of your security posture. Document your findings and use them to drive continuous improvement. Staying proactive helps you stay ahead of attackers and keeps your cloud environment secure.
Stay Informed About Threats and Best Practices
The world of cloud security is always changing. New threats and vulnerabilities emerge regularly, so it’s important to stay informed. Subscribe to updates from trusted sources such as government agencies, security organizations, and technology vendors. Participate in industry groups or forums to learn from peers and share experiences. Regularly review and update your identity controls based on the latest guidance and threat intelligence. This helps ensure your cloud environment remains protected against both old and new risks.
Conclusion
Improving identity controls in cloud systems is vital for protecting sensitive data and maintaining trust. By following these easy steps, organizations can strengthen their defenses and reduce the risk of unauthorized access. Regular reviews, strong policies, and employee education will help keep your cloud environment secure. As cloud threats evolve, staying proactive and informed is the best way to ensure your organization s security.
FAQ
Why are identity controls important in cloud systems?
Identity controls help prevent unauthorized access and protect sensitive data by ensuring only approved users can access cloud resources.
What is multi-factor authentication?
Multi-factor authentication requires users to provide two or more forms of proof before accessing accounts, making it harder for attackers to gain entry.
How often should user permissions be reviewed?
User permissions should be reviewed at least quarterly, or whenever an employee changes roles or leaves the organization.
What is the principle of least privilege?
The principle of least privilege means giving users only the access they need to do their jobs, reducing the risk if an account is compromised.
How can automation help with identity controls?
Automation enforces policies, manages permissions efficiently, and helps detect suspicious activities, making identity management more reliable and secure.